Can Hurricane Dorian Strengthen Again Now That Its Moving Over Warm Water
Hurricane Dorian: Path of destruction
- Published
Image source, Getty Images
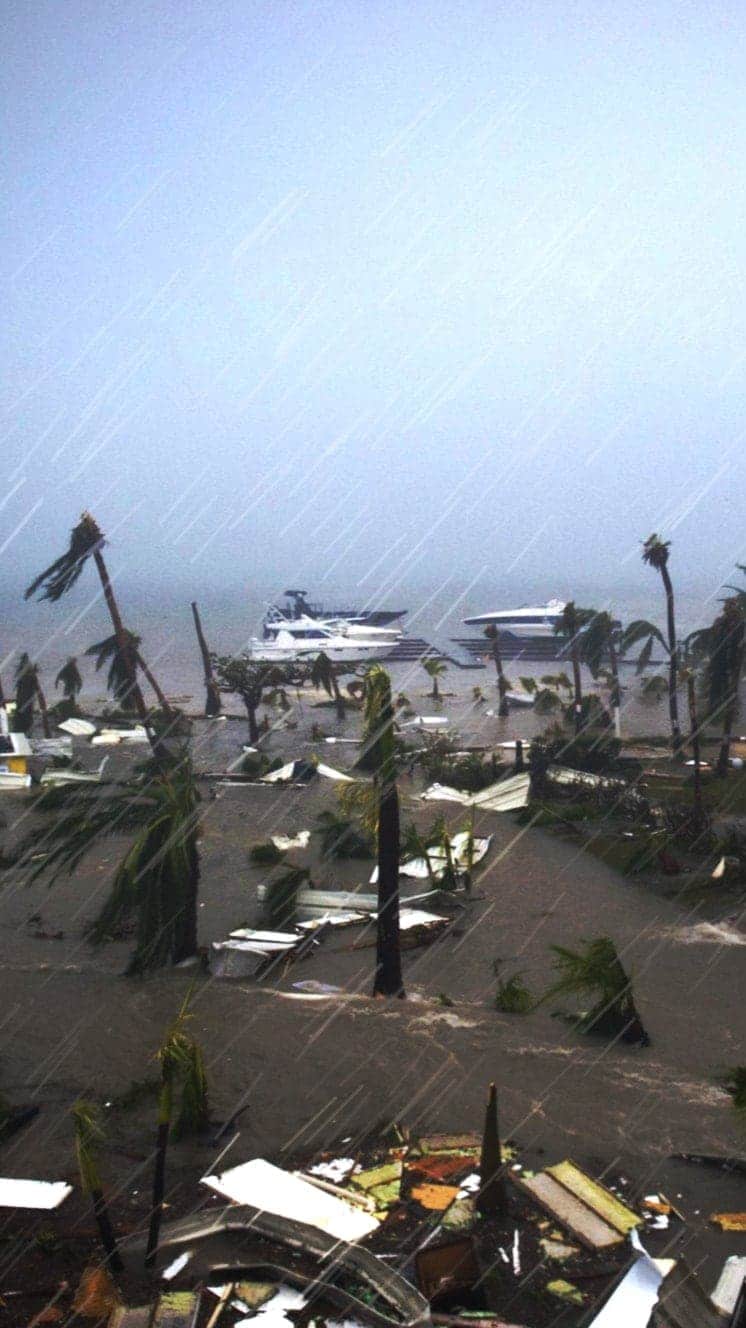
Hurricane Dorian - the almost powerful storm to hit the Bahama islands since records began - has left widespread devastation, at least 43 expressionless and many more than still missing days after the storm passed.
Powerful winds, rain and surges of ocean water acquired by the category five storm pummelled the islands for 3 days as it slowly edged towards the U.s..
The storm then headed northwards, triggering warnings of loftier winds and storm surges in the Carolinas before battering Canada's Nova Scotia province as a mail-tropical cyclone - withal driving winds of 100mph (160km/h).
Where has been hit?
When Dorian hit the Abacos Islands in the north of the Bahamas on 1 September, sustained winds reached 185mph (298km/h).
The master towns were flooded by storm surges, metres above normal body of water levels. The powerful winds and water ripped houses apart, tore boats from moorings and dragged vehicles and debris across the islands.
At least 43 people died as a result - 35 in the Abaco Islands and 8 in Yard Bahama, just numbers are expected to exist much higher as hundreds of people are notwithstanding missing.
Dorian's slow progress - merely one mile an hour at times - full-bodied the storm over the islands, exacerbating the extent of the impairment.
On the Abacos, thousands of houses were levelled, telecommunications torn down and roads and wells damaged, the United nations reports.
Bahamas Government minister of National Security Marvin Dames said the devastation in the Abaco Islands' Marsh Harbour was "beyond what anyone tin can imagine".
"Many of the homes take been totally destroyed and and then we're going to certainly need, every bit a government, and a people, a massive rebuilding strategy, a plan, after all of this. It's very pitiful."
The authorities has warned the death cost will exist "staggering".
Aeriform images over the Abacos showed miles of destruction, with roofs torn off, scattered debris, overturned cars, shipping containers and boats, and high water levels.
The worst-hit isle, Great Abaco, is described every bit nearly uninhabitable, with no water, power or nutrient, and militias patrolling the streets to stop looting.
Survivor Ramond King, from Marsh Harbour, said everything was gone.
"Yes, I did witness the storm, I was in the front room and I watched a tornado behave my roof," he told Reuters. "I was but in that location, like: this can't exist real, this can't exist existent."
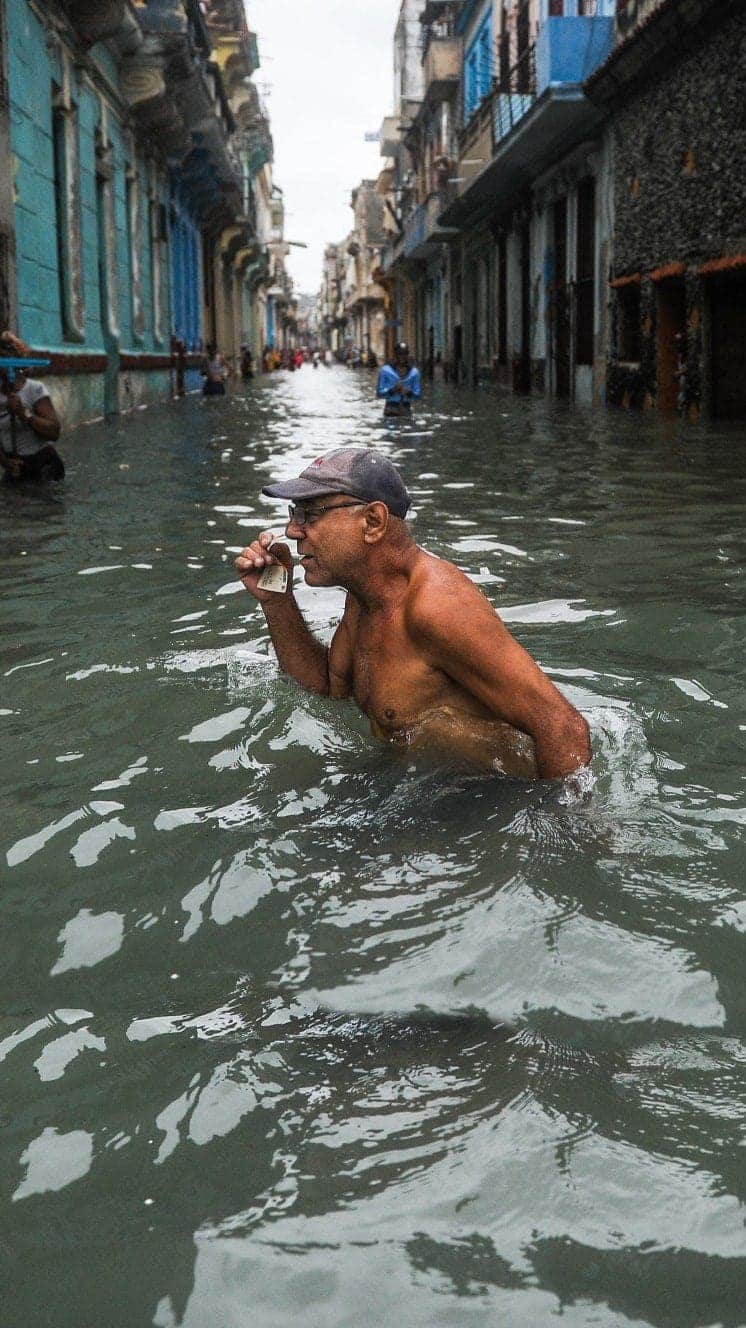
Many people in Grand Bahama were forced to abscond to the roofs of their homes to escape the ascension alluvion waters, which covered most of the island at i phase. Floods levels are now said to be receding.
Prime Government minister Minnis said while in that location was widespread destruction, "what was near significant, those homes that were built on stilts were not damaged".
Rescue, relief and recovery operations are now under way. Cruise liners, private planes and helicopters were all being used to assist those however trapped in the Abaco Islands and Grand Bahama.
International efforts include assistance from the Royal Navy'due south RFA Mounts Bay and HMS Protector, and nine cutters from the US Coast Guard.
Some survivors take been taken to Florida or Nassau, further southward in the Bahamas.
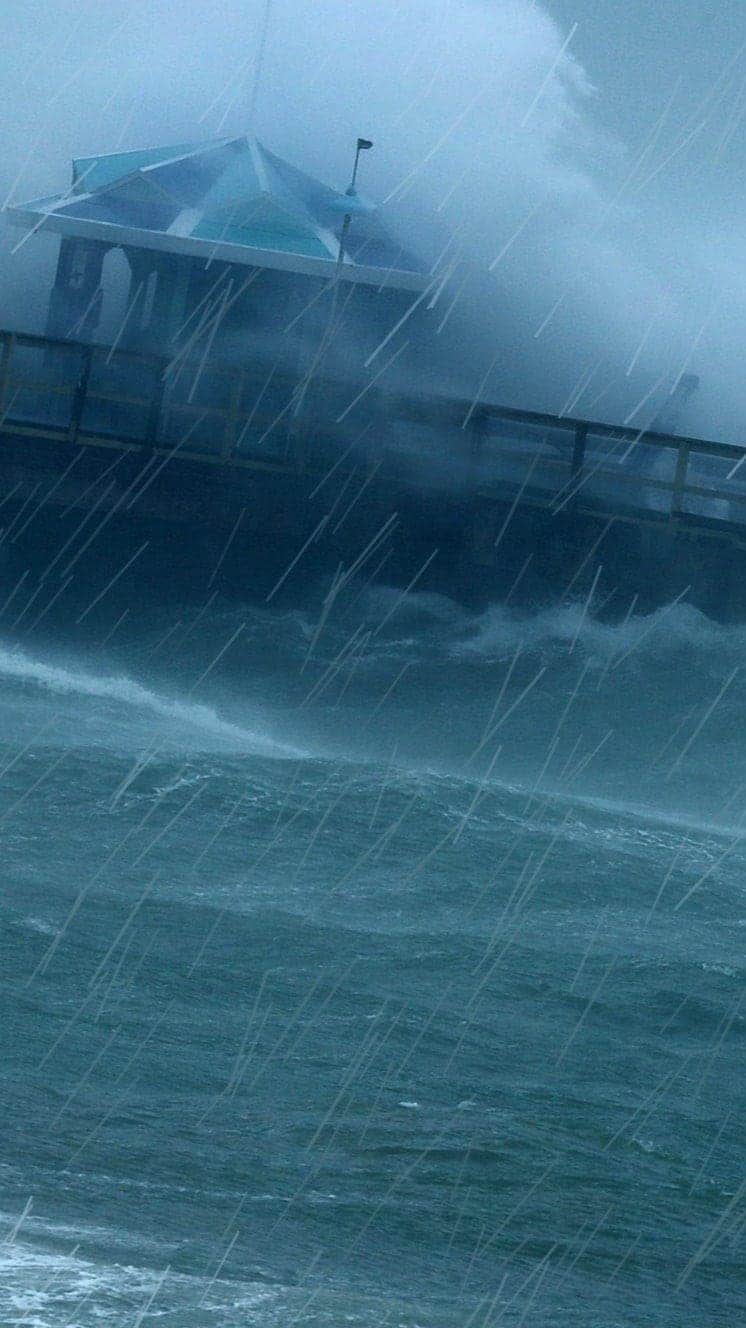
Devastating storm surges
As well as dangerous wind speeds, authorities issued warnings of life-threatening tempest surges along the whole length of the coasts of Georgia, S Carolina and North Carolina as Dorian left the Bahamas.
Thousands took shelter in Carmine Cross and community evacuation shelters in the The states declension states every bit a precaution.
Tempest surges are caused when huge volumes of h2o are pushed by hurricane-force winds. When they meet land, the water surges inshore at levels far exceeding normal tides.
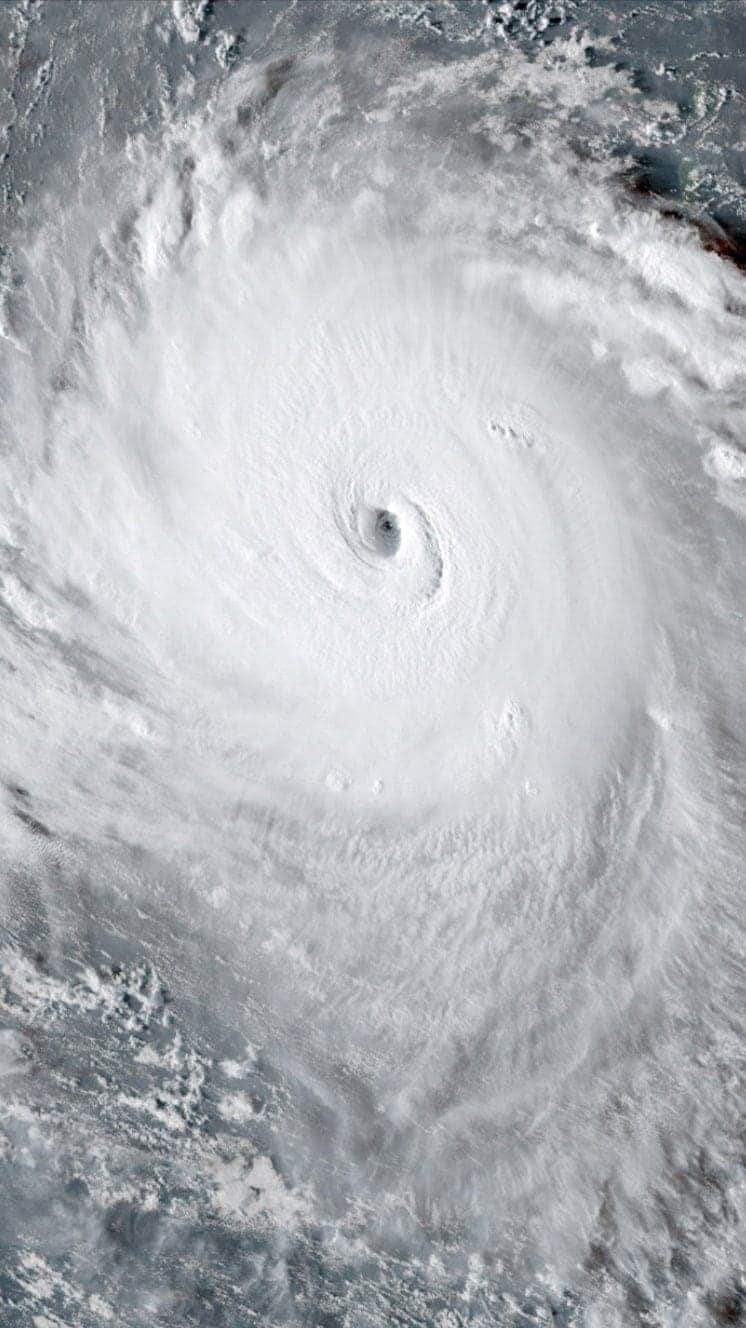
Dorian'southward strength
At category five, Dorian was the 2d-strongest Atlantic hurricane on record, with some gusts reaching 200mph (321km/h). It is the 5th Atlantic hurricane to reach the highest category in the last 4 years.
Hurricane Irma in 2022 was besides category five and caused widespread damage across the Leeward Islands, Caribbean and Florida keys, dissentious roads, buildings, airports and harbours.
Thousand Bahama was also hitting past category five Hurricane Matthew in 2022 - many residents had nonetheless to fully rebuild their houses before Dorian'southward arrival.
How hurricanes happen
Hurricanes

A guide to the world's deadliest storms


Hurricanes are violent storms that can bring devastation to coastal areas, threatening lives, homes and businesses.
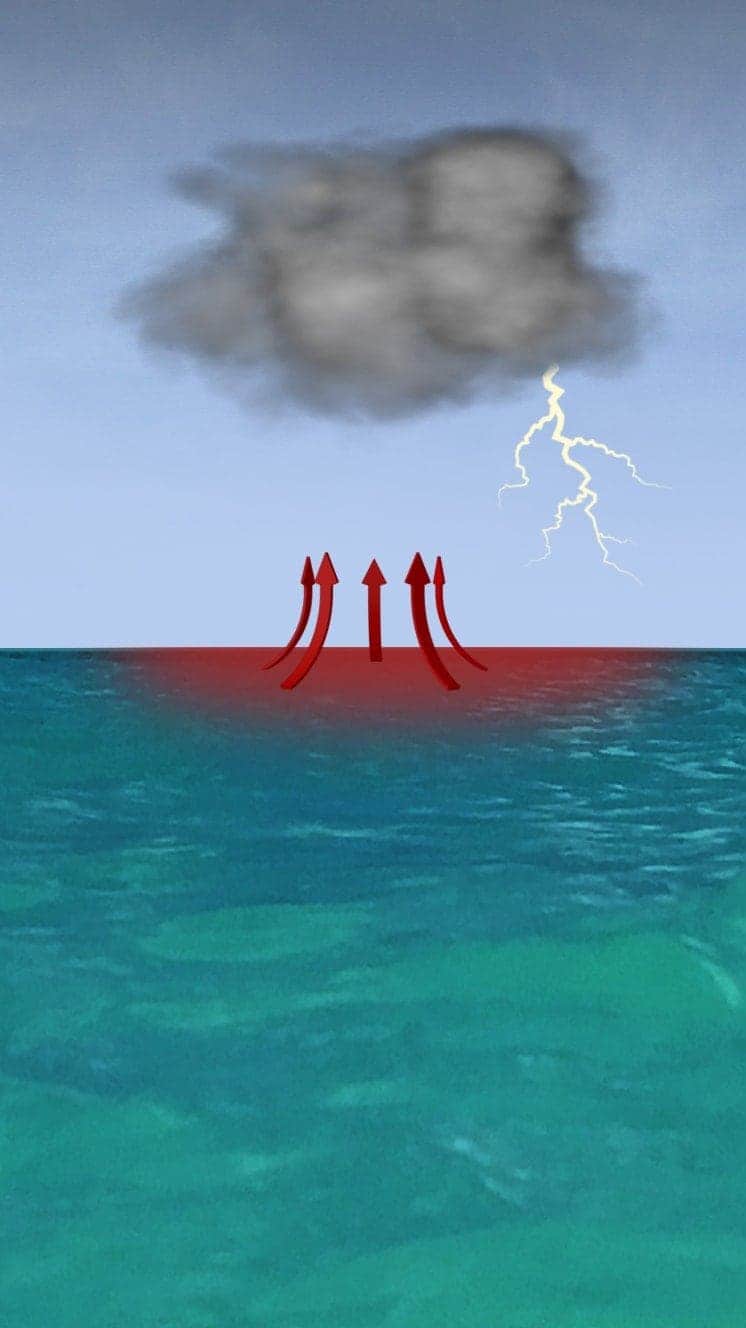
Hurricanes develop from thunderstorms, fuelled by warm, moist air as they cross sub-tropical waters.
Warm air rises into the tempest.

Air swirls in to fill up the low pressure in the tempest, sucking air in and upwards, reinforcing the low pressure level.

The storm rotates due to the spin of the earth and energy from the warm ocean increases wind speeds as information technology builds.
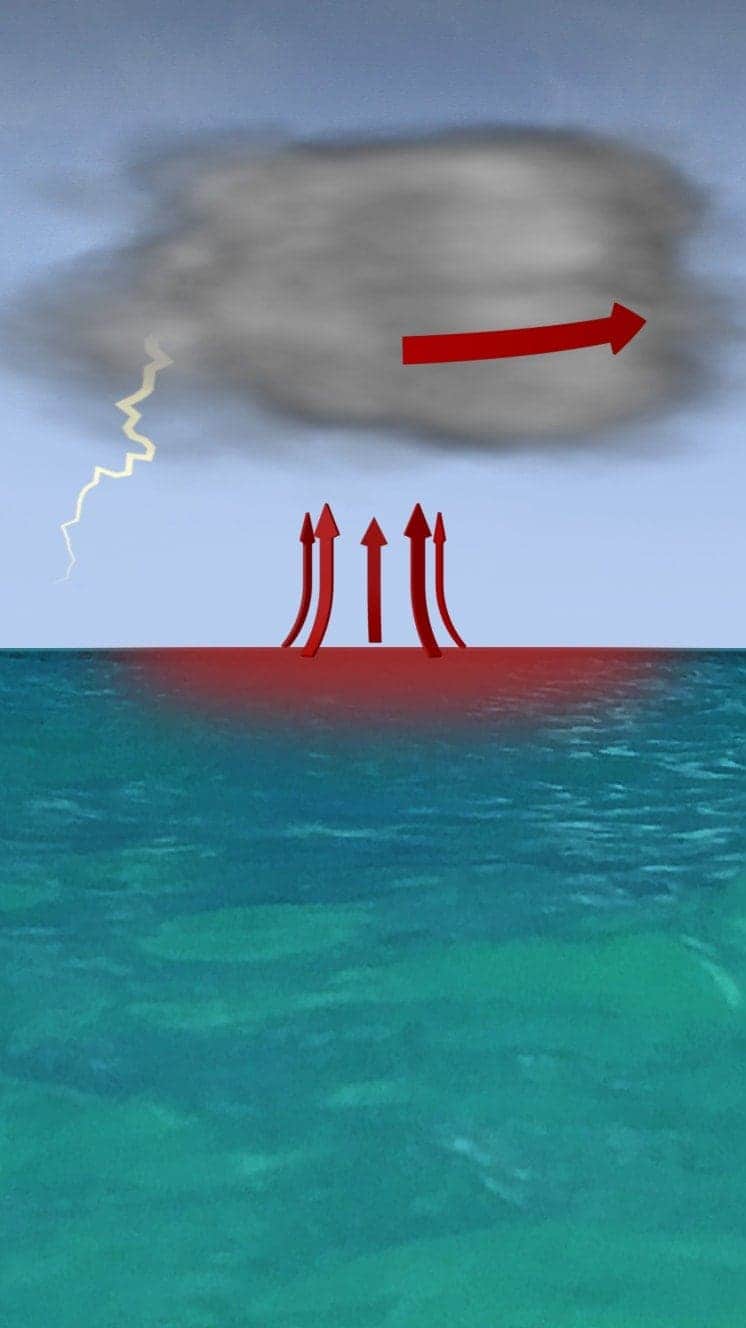
When winds achieve 119km/h (74mph), information technology is known as a hurricane - in the Atlantic and Eastern Pacific - or a typhoon in the Western Pacific.

"Everybody has a programme until they get punched in the face. Well, we're about to become punched in the face."
Florida Mayor Bob Buckhorn, ahead of Hurricane Irma (2017)

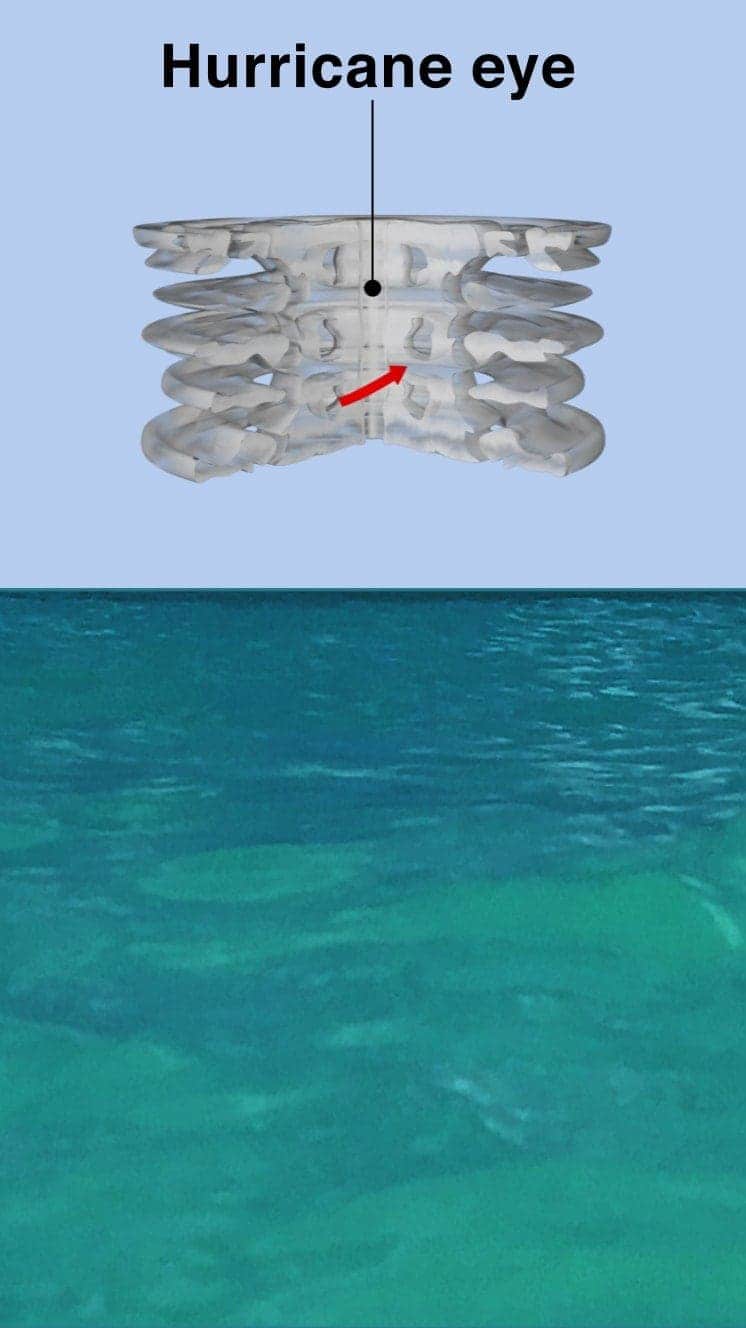
The fundamental center of calmer weather is surrounded past a wall of rainstorms.
This eyewall has the fastest winds below it and trigger-happy currents of air rising through it.

A mound of h2o piles up below the heart which is unleashed as the storm reaches land.
These tempest surges can cause more than damage from flooding than the winds.

"Urgent warning almost the rapid rise of water on the SW FL coast with the passage of #Irma's eye. MOVE Away FROM THE WATER!"
Tweet from the National Hurricane Center

The size of hurricanes is mainly measured by the Saffir-Simpson scale - other scales are used in Asia Pacific and Australia.

Winds 119-153km/h
Some small flooding, little structural damage.
Storm surge +ane.2m-1.5m

Winds 154-177km/h
Roofs and trees could be damaged.
Storm surge +1.8m-2.4m

Winds 178-208km/h
Houses suffer damage, severe flooding
Storm surge +2.7m-3.7m
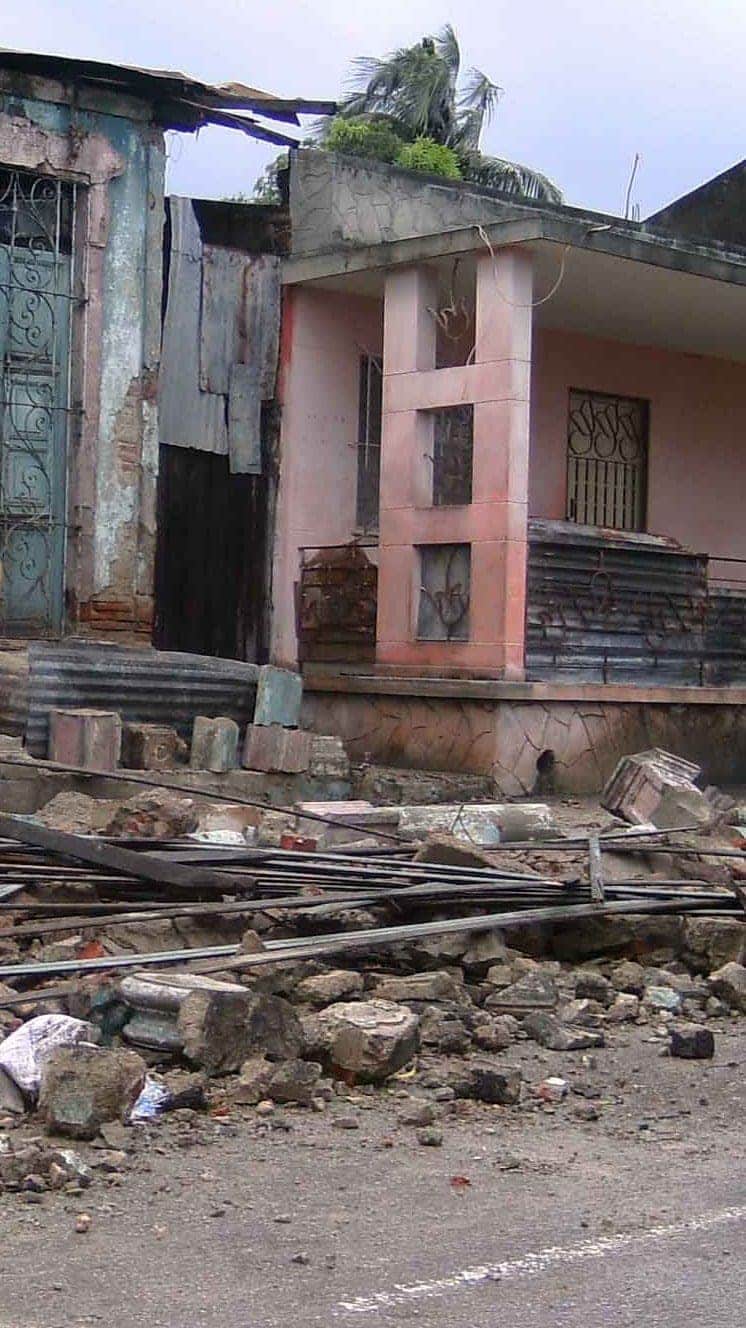

Hurricane Sandy (2012) caused $71bn damage in the Caribbean and New York

Winds 209-251km/h
Some roofs destroyed and major structural damage to houses.
Tempest surge +4m-5.5m
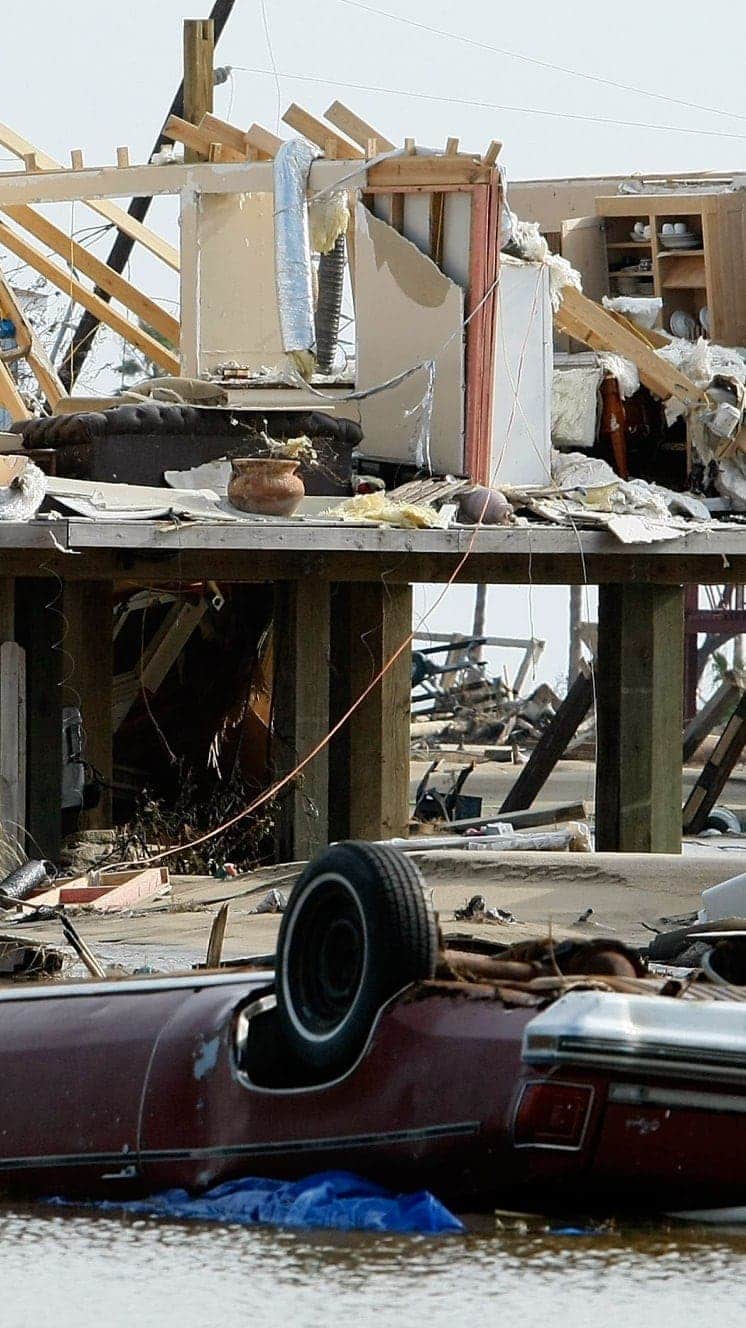

Hurricane Ike (2008) striking Caribbean area islands and Louisiana and was blamed for at least 195 deaths

Winds 252km/h+
Serious damage to buildings, severe flooding further inland.
Tempest surge +5.5m
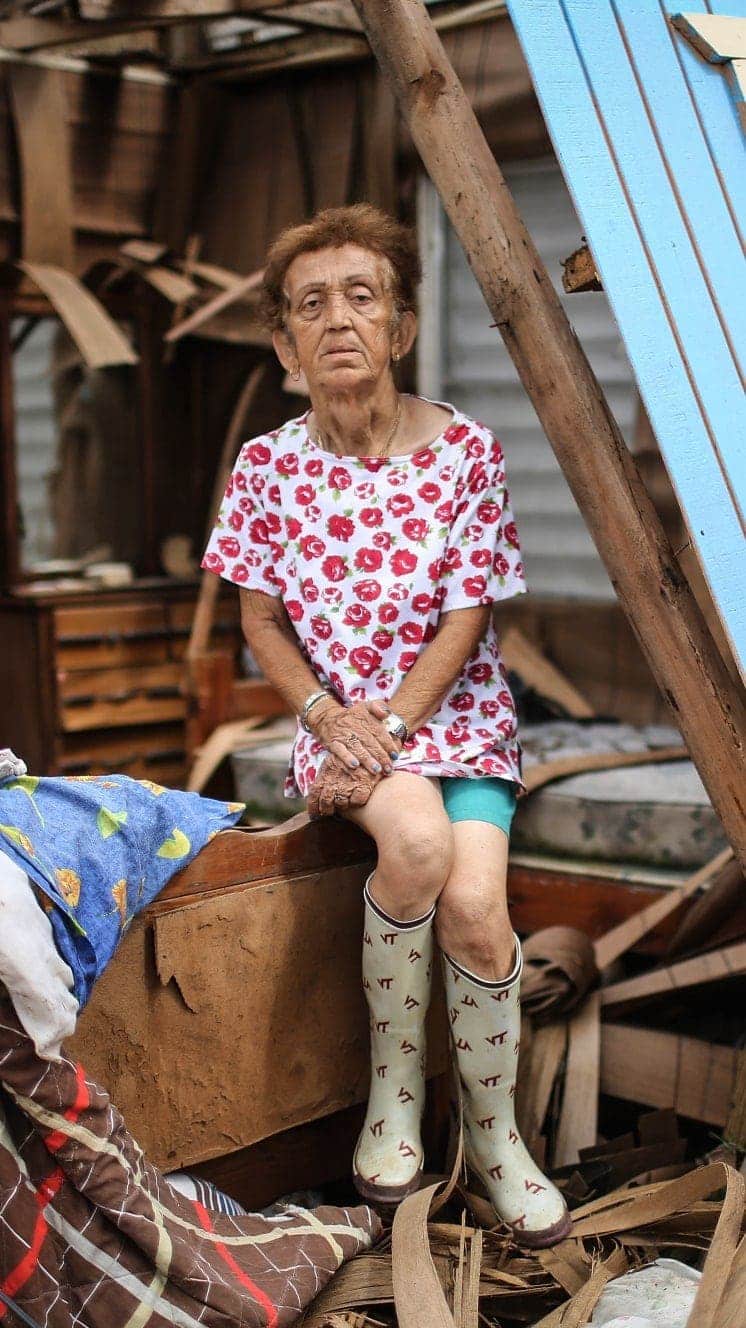

Hurricane Irma (2017) caused devastation in Caribbean islands, leaving thousands homeless
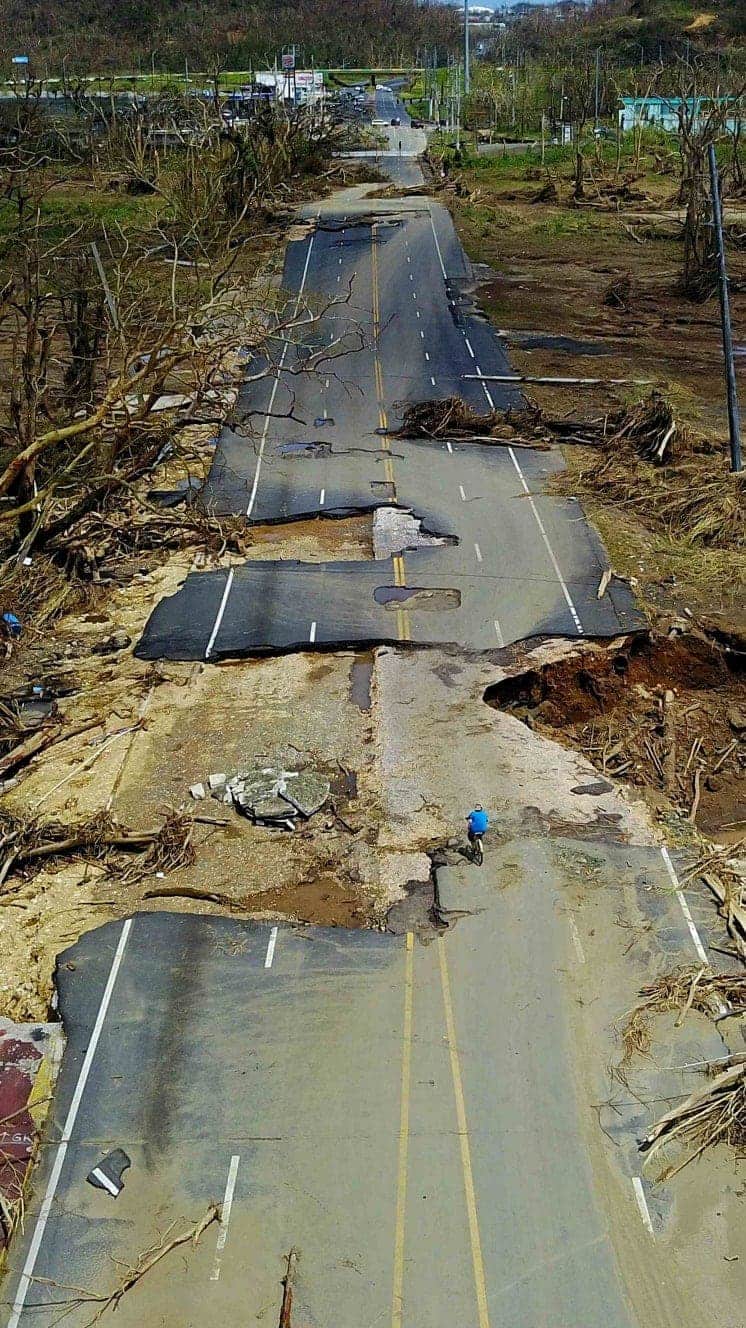

"For everyone thinking they can ride this storm out, I have news for yous: that will be one of the biggest mistakes you can make in your life."
Mayor of New Orleans Ray Nagin ahead of Hurricane Gustav, 2008
Source: https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-49553770
0 Response to "Can Hurricane Dorian Strengthen Again Now That Its Moving Over Warm Water"
Post a Comment